
If you’re involved with Bitcoin, you’re probably aware of the SPAM War that is underway. Bitcoin Core wants to change the limit on OP_RETURN from 80 bytes to 100,000 bytes in the soon to be released v30, in effect opening Bitcoin up to a lot of unnecessary data being included in block transactions that has nothing to do with the financial transaction itself. This forces node runners to host and transmit this extra data on their nodes as well as filling up the blocks with garbage and raising fees for transactions. There is also the historical precedent that child porn, abuse content could be added to compromise people hosting nodes causing fear of prosecution from having this material on their computers in their home or business (CSAM has already been hidden in the blockchain but obfuscated to where there is plausible deniability, as it takes a forensic style effort to retrieve). This would drive nodes to major crypto megacorps in the space that could filter this material or be granted legal indemnification to host the blockchain with this data. Personally, I see it as a way to damage Bitcoin at the time stablecoins are ramping up to sell national debt along with maybe driving banking towards Ethereum which is already compromised.
So with that background out of the way, Bitcoin Knots is the Bitcoin community’s defense against the co-opted Bitcoin Core Devs trying to implement this campaign against Bitcoin, as Bitcoin Knots filters current SPAM transactions along with limiting OP_RETURN to 40 bytes. Also, Bitcoin Knots grants node runners the ability to configure a lot of options which Bitcoin Core is removing as they are trashing node runners in favor of miners. So anyone who values Bitcoin and wants to ensure this fails like the Bitcoin Cash attempted hard fork, run Bitcoin Knots to send a message to Bitcoin Core devs.
One note, as I compile my Bitcoin Knots binaries, I used the following for my node.
cmake -B build -DWITH_ZMQ=ON -DWITH_GUI=OFF
cmake --build build -j 1The -j 1 flag limited it to just one CPU on my Raspberry Pi 5 as the first attempt using more cores exited with an error. I had also deleted the source and did a fresh clone from Github, so that might have been a problem with doing a pull and switching to the proper branch. Consequently, this version is changing the way it’s compiled. And because it’s a headless Pi I didn’t need the GUI. And a single CPU for compiling was good since the node was still up and running in the background, and it still didn’t take that long to compile on my Pi 5. My backup Bitcoin server is on a 24 thread server with 8 dedicated CPUs and compiled without a hitch with half the CPUs, but that machine isn’t always on and only run every other day to stay up with the blockchain.
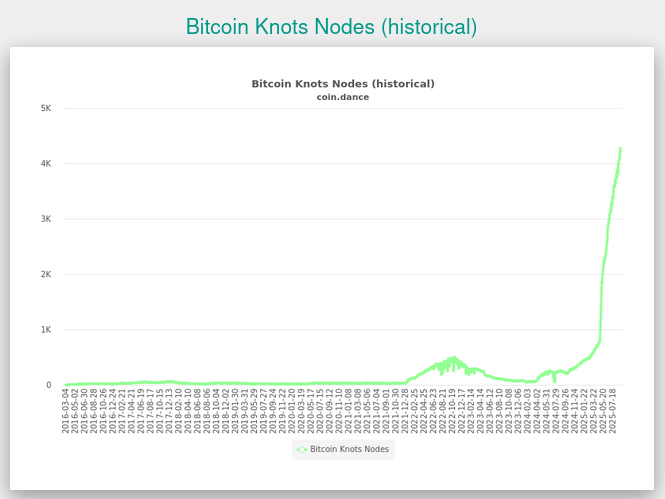
And on the positive, Bitcoin Knots is up to 18.2% of reachable nodes at the moment. And we don’t have to fear v30 of Bitcoin Core quite yet, as very few nodes run the latest Bitcoin Core software anyway. But this resistance to the gaslighting of Bitcoin Core devs sends a powerful message which could end up moving towards a fork down the road if they don’t respect users and pull back on these attempts to undermine the Bitcoin Core protocol. Below I’ll include the top clients from my Raspberry Pi 5 node as currently connected which I limit to 40 connections to not interfere with my home network too much, and it also runs the Lightning Network Daemon as well with its connections (I also run a Monero Node on another Pi 5 limited to 80 connections).
https://github.com/bitcoinknots/bitcoin/blob/v29.1.knots20250903/doc/release-notes.md
Bitcoin Knots version 29.1.knots20250903 is now available from:
https://bitcoinknots.org/files/29.x/29.1.knots20250903
This release includes new features, various bug fixes and performance improvements, as well as updated translations.
Please report bugs using the issue tracker at GitHub:
https://github.com/bitcoinknots/bitcoin/issues
To receive security and update notifications, please subscribe to:
https://bitcoinknots.org/list/announcements/join
How to Upgrade
If you are running an older version, shut it down. Wait until it has completely shut down (which might take a few minutes in some cases), then run the installer (on Windows) or just copy over /Applications/Bitcoin-Qt (on macOS) or bitcoind/bitcoin-qt (on Linux).
Upgrading directly from very old versions of Bitcoin Core or Knots is possible, but it might take some time if the data directory needs to be migrated. Old wallet versions of Bitcoin Knots are generally supported.
Compatibility
Bitcoin Knots is supported on operating systems using the Linux kernel, macOS 13+, and Windows 10+. It is not recommended to use Bitcoin Knots on unsupported systems.
Known Bugs
In various locations, including the GUI’s transaction details dialog and the "vsize" result in many RPC results, transaction virtual sizes may not account for an unusually high number of sigops (ie, as determined by the -bytespersigop policy) or datacarrier penalties (ie, -datacarriercost). This could result in reporting a lower virtual size than is actually used for mempool or mining purposes.
Due to disruption of the shared Bitcoin Transifex repository, this release still does not include updated translations, and Bitcoin Knots may be unable to do so until/unless that is resolved.
Notable changes
P2P and Network Changes
- libnatpmp has been replaced with a built-in implementation of PCP and NAT-PMP (still enabled or disabled using the
-natpmpoption). This supports automatic IPv4 port forwarding as well as IPv6 pinholing. (#30043) - NAT-PMP is now enabled by default. This means nodes with
-listenenabled (the default) but running behind a firewall, such as a local network router, will be reachable if the firewall/router supports either of thePCPorNAT-PMPprotocols. It can be turned off with the-natpmp=0option. (#33004) - Upon receiving an orphan transaction (an unconfirmed transaction that spends unknown inputs), the node will attempt to download missing parents from all peers who announced the orphan. This change may increase bandwidth usage but make orphan-handling more reliable. (#31397)
- In addition to the count-based
-blockreconstructionextratxnlimit on cached transactions not accepted for relaying, a new-blockreconstructionextratxnsizeoption has been added to set an upper limit on the total memory usage consumed by this cache (10 MB by default). - The default
-blockreconstructionextratxnlimit is increased to 32768 transactions. -peerbloomfiltersis now restricted to localhost by default. If you use BIP37 wallet software remotely, you should use the-whitelist bloomfilter@<IP>configuration. You can also set-peerbloomfilters=0to disable it for localhost, or-peerbloomfilters=1if you wish to provide the service to the entire network. If you wish to offer it publicly, do note that this service can be resource-intensive.
Mempool Policy and Mining Changes
- The
-maxscriptsizepolicy now applies to the entire witness stack of each input, to address attempts to evade overly-specific targetting. - Ephemeral anchors is a new concept that allows a single dummy recipient in a transaction, provided the transaction is zero fee and the “anchor” is immediately sent in another transaction broadcast together with it. This allows for smart contracts such as Lightning where neither party can unilaterally increase the transaction fee, yet using an anchor can create a followup adding the necessary fee. (#30239) By default, these anchors are accepted by Bitcoin Knots if and only if they are minimal size and zero value. If you want a more flexible policy (allowing for dummy sends and/or dust amounts), or wish to reject these new anchors entirely, you can use the new
-permitephemeraloption. There is also a-permitbareanchoroption which permits (or forbids) transaction that do not have real recipients (only an anchor). (knots#136) - A new
-permitbaredatacarrieroption (default 0 / not permitted) has been added to control acceptance of transactions with only a datacarrier output and no real recipients. This is sometimes used to burn bitcoins. (knots#136) - The maximum number of potentially executed legacy signature operations in a single standard transaction is now limited (by default) to 2500. Signature operations in all previous output scripts, in all input scripts, as well as all P2SH redeem scripts (if there are any) are counted toward the limit. (#32521) It can be configured with the
-maxtxlegacysigopsoption. - A new option
-acceptunknownwitnesshas been provided to filter transactions sending to/using unknown/future witness script versions. While this should generally be safe, it will also affect batch transactions, which may be created be unsuspecting third parties who do not pay attention to the witness version of addresses they send to (this is considered a best practice). For that reason, the new filter is not enabled by default, and if you wish to use it, you must set-acceptunknownwitness=0in your configuration. - Two new options,
-minrelaycoinblocksand-minrelaymaturity, have been added to restrict transactions relayed/mined to only ones spending bitcoins with some degree of settlement. The former measures the value of bitcoins being spent at a rate of 1 BTC per block since their confirmation, while the second is a strict block-based maturity metric. In both cases, the minimum must be met by transactions before the node will relay or mine them. These are both disabled by default. (knots#148) - Several policy filters exist to make future protocol changes safer, collectively classified as “non-mandatory-script-verify-flag” rejections. Unlike other policies, previous versions of Bitcoin Knots did not allow disabling these filters. However, this makes recovery difficult when people accidentally lock their bitcoins behind filtered “upgradable opcodes”, and to accomidate recovery, this version of Knots allows specifying these rejection reasons to the
ignore_rejectsparameter ofsendrawtransaction, thereby overriding the rejection on a per-transaction basis (as with other filters). Please be responsible with this feature, and note that using it during a network upgrade may result in creating invalid blocks and lost mining rewards! - The
-rejecttokensand datacarrier-related policies have been updated to detect “OLGA” spam. (knots#151)
GUI changes
- The configured “font for amounts” is now consistently used for all monetary amounts in the GUI.
- The embedded “Roboto Mono Bold” font has been replaced with a new “OCR-Bitcoin” font created specifically for Bitcoin Knots.
- Qt 6.2+ is now supported as an alternative to Qt 5.15 (which remains the default for precompiled releases). As the Qt project no longer supports version 5.15, it will likely be removed in a future release. To build the source code using Qt 6, specify -D WITH_QT_VERSION=6 to your cmake command line.
- Support for ᵇTBC and ˢTBC units has been removed, since Bitcoin’s value has made them largely unnecessary. The basic TBC unit is now available to all users without jumping through hoops to install a new Tonal-enabled font. See the Bitcoin Wiki page on Tonal Bitcoin to learn more about the (eccentric) tonal bitcoin unit(s).
Logging
Unconditional logging to disk is now rate limited by giving each source location a quota of 1MiB per hour. Unconditional logging is any logging with a log level higher than debug, that is info, warning, and error. All logs will be prefixed with [*] if there is at least one source location that is currently being suppressed. (#32604)
When -logsourcelocations is enabled, the log output now contains the entire function signature instead of just the function name. (#32604)
Updated RPCs
- The RPC
testmempoolacceptresponse now includes areject-detailsfield in some cases, similar to the complete error messages returned bysendrawtransaction(#28121) - Duplicate blocks submitted with
submitblockwill now persist their block data even if it was previously pruned. If pruning is activated, the data will be pruned again eventually once the block file it is persisted in is selected for pruning. This is consistent with the behaviour ofgetblockfrompeerwhere the block is persisted as well even when pruning. (#31175) getmininginfonow returnsnBitsand the current target in thetargetfield. It also returns anextobject which specifies theheight,nBits,difficulty, andtargetfor the next block. (#31583)getblockandgetblockheadernow return the current target in thetargetfield (#31583)getblockchaininfoandgetchainstatesnow returnnBitsand the current target in thetargetfield (#31583)- The newly-unhidden
waitfornewblock(which simply does not return until a new block has been received) now takes an optionalcurrent_tipargument to avoid a potential race between the new block and the RPC call. If provided, the RPC will return immediately if the best block already does not match. (#30635) waitforblock(which waits for a specific block hash before returning) andwaitforblockheight(which waits for a given height to be reached) are no longer hidden. (#30635)- The
getblocktemplateRPCmintime(BIP23) field now accounts for the timewarp fix proposed in BIP94 on all networks. This ensures that, in the event a timewarp fix softfork activates on Bitcoin, un-upgraded miners will not accidentally violate the timewarp rule. As a reminder, it’s important that any software which uses thegetblocktemplateRPC takes these values into account (eithercurtimeormintimeis fine). Relying only on a clock can lead to invalid blocks under some circumstances, especially once a timewarp fix is deployed. (#31600) - The
gettxoutproofandverifytxoutproofmethods have been extended with a new Segwit-aware mode (enabled withprove_witnessandverify_witnessnamed options, respectively). In this mode, the proofs prove the “witness txid” (wtxid) instead of the traditional transaction id (txid). The format of these proofs is currently considered experimental and may be changed in future versions. (#32844) getpeerinfonow includeslast_block_announcementfor each peer, for the most recent time that peer has been the first to notify the local node of a new block (or zero if it has never been the first). (#27052)- The
dumptxoutsetRPC now requires atypeparameter to be specified. To have the same behavior before v29, use the “latest” parameter. (#30808)
Changes to wallet-related RPCs can be found in the Wallet section below.
Updated REST APIs
GET /rest/block/<BLOCK-HASH>.jsonandGET /rest/headers/<BLOCK-HASH>.jsonnow return the current target in thetargetfield- A new REST API endpoint (
/rest/spenttxouts/BLOCKHASH) has been introduced for efficiently fetching spent transaction outputs using the block’s undo data. (#32540)
Wallet
- The
walletcreatefundedpsbtRPC method will now set a recent block height as the transaction lock time, if a lock time is not otherwise provided, to discourage miners from attempting to fee-snipe. bumpfeeas well aspsbtbumpfeenow offer arequire_replacableparameter which can be set to false to bump the fee on transactions that do not signal BIP125 transaction replacability. Bumping fees in the GUI will likewise allow non-signalling transactions, with a warning. (#31953) It is expected that therequire_replacableparameter may default to false in the future, or perhaps even be removed entirely.- When bumping transaction fees in the GUI, the “Create Unsigned” option now opens the PSBT Operations dialog rather than simply copying the raw PSBT to the clipboard directly.
Updated Settings
- The
-rpcuserand-rpcpasswordsettings are no longer considered deprecated, and are expected to remain supported for the immediate future. (#32423) - Previously,
-proxyspecified the proxy for all networks (except I2P which uses-i2psam) and only the Tor proxy could have been specified separately via-onion. Now, the syntax of-proxyhas been extended and it is possible to specify separately the proxy for IPv4, IPv6, Tor and CJDNS by appending=followed by the network name, for example-proxy=127.0.0.1:5555=ipv6configures a proxy only for IPv6. The-proxyoption can be used multiple times to define different proxies for different networks, such as-proxy=127.0.0.1:4444=ipv4 -proxy=10.0.0.1:6666=ipv6. Later settings override earlier ones for the same network; this can be used to remove an earlier all-networks proxy and use direct connections only for a given network, for example-proxy=127.0.0.1:5555 -proxy=0=cjdns. (#32425) - The
-maxmempoolstartup parameter is now capped on 32-bit systems to 500MB. (#32530) - Handling of negated
-noseednode,-nobind,-nowhitebind,-norpcbind,-norpcallowip,-norpcwhitelist,-notest,-noasmap,-norpcwallet,-noonlynet, and-noexternalipoptions has changed. Previously negating these options had various confusing and undocumented side effects. Now negating them just resets the settings and restores default behaviors, as if the options were not specified. - As a safety check, Bitcoin Knots will fail to start when
-blockreservedweightinit parameter value is lower than2000weight units. Bitcoin Knots will also fail to start if the-blockmaxweightor-blockreservedweightinit parameter exceeds consensus limit of4,000,000 WU. - Passing
-debug=0or-debug=nonenow behaves like-nodebug: previously set debug categories will be cleared, but subsequent-debugoptions will still be applied.
Tools and Utilities
bitcoin-cli -netinfonow includes information about CPU time processing messages to/from each peer. (#31672)bitcoin-cliwill now just do the right thing if passed a block hash to height-or-hash parameters forgettxoutsetinfo,dumptxoutset, andgetblockstats. (#33230)
Build System
The build system has been migrated from Autotools to CMake:
- The minimum required CMake version is 3.22.
- In-source builds are not allowed. When using a subdirectory within the root source tree as a build directory, it is recommended that its name includes the substring “build”.
- CMake variables may be used to configure the build system. See Autotools to CMake Options Mapping for details.
- For single-configuration generators, the default build configuration (
CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE) is “RelWithDebInfo”. However, for the “Release” configuration, CMake defaults to the compiler optimization flag-O3, which has not been extensively tested with Bitcoin Knots. Therefore, the build system replaces it with-O2. - By default, the built executables and libraries are located in the
bin/andlib/subdirectories of the build directory. - The build system supports component‐based installation. The names of the installable components coincide with the build target names. For example:
cmake -B build
cmake --build build --target bitcoind
cmake --install build --component bitcoind
- If any of the
CPPFLAGS,CFLAGS,CXXFLAGSorLDFLAGSenvironment variables were used in your Autotools-based build process, you should instead use the corresponding CMake variables (APPEND_CPPFLAGS,APPEND_CFLAGS,APPEND_CXXFLAGSandAPPEND_LDFLAGS). Alternatively, if you opt to use the dedicatedCMAKE_<...>_FLAGSvariables, you must ensure that the resulting compiler or linker invocations are as expected.
For more detailed guidance on configuring and using CMake, please refer to the official CMake documentation and CMake’s User Interaction Guide. Additionally, consult platform-specific doc/build-*.md build guides for instructions tailored to your operating system.
Software Expiration
Since v0.14.2.knots20170618, each new version of Bitcoin Knots by default expires 1-2 years after its release (during November). This is a security precaution to help ensure nodes remain kept up to date.
New in this version, Bitcoin Knots will provide a warning 4 weeks prior to expiry and send an alert (see -alertnotify). When the expiry is reached, the warning will be updated and another alert sent. Mining will also be disabled at that time.
This is an optional feature. You may disable it by setting softwareexpiry=0 in your config file, but this is strongly discouraged without some other form of update reminders. You may also set softwareexpiry to any other POSIX timestamp, to trigger an expiration at that time instead.
Low-Level Changes
Consensus
- Previously, if a node was restarted during a block race (two parallel blocks with equally best work), there was a random chance the node would switch to a different one than it had chosen prior to the restart. This has changed so that the currently-active chain remains the same. (#29640)
Tools and Utilities
- A new tool
utxo_to_sqlite.pyconverts a compact-serialized UTXO snapshot (as created with thedumptxoutsetRPC) to a SQLite3 database. Refer to the script’s--helpoutput for more details. (#27432)
Service definitions
- The included OpenRC service has been adapted to FHS 3.0 and provides a new BITCOIND_LOGDIR variable to control where the debug.log file is written.
- The OpenRC service will now give the RPC cookie file group-readable access, so that other programs running in the $BITCOIND_GROUP (by default, ‘bitcoin’) can access the RPC server automatically.
- The OpenRC service starts bitcoind in the background, and only becomes active (to trigger dependent services) when the node and RPC server has initialised. This ensures the node is accessible before any services relying on it start, without blocking other unrelated system services. (#24066)
Stability
- During initial synchronisation (as well as reindexing), the node will now write its progress to disk at least once an hour, instead of the previous 24 hour wait on systems with lots of memory and large dbcache configuration. This should avoid as much lost progress in the event of interruption, and improve shutdown speeds. (#30611, #32414)
Tests
- The BIP94 timewarp attack mitigation (designed for testnet4) is no longer active on the regtest network. (#31156)
Dependencies
- Building the GUI from source now requires rsvg-convert (often packaged as librsvg2-bin, librsvg2-tools, or simply librsvg), ImageMagick (except on macOS), and libicns (only for macOS).
- libnatpmp has been removed as a dependency (#31130, #30043).
Credits
Thanks to everyone who directly contributed to this release:
- 0xB10C
- achow101
- Adlai Chandrasekhar
- Afanti
- Alfonso Roman Zubeldia
- am-sq
- Andre
- Andre Alves
- Andrew Toth
- Anthony Towns
- Antoine Poinsot
- Ash Manning
- Ataraxia
- Ava Chow
- benthecarman
- bigspider
- Boris Nagaev
- Brandon Odiwuor
- Bufo
- brunoerg
- Chris Stewart
- Cory Fields
- costcould
- Crypt-iQ
- Daniel Pfeifer
- Daniela Brozzoni
- David Gumberg
- deadmanoz
- dergoegge
- enirox001
- epysqyli
- espi3
- Eval EXEC
- Fabian Jahr
- fanquake
- furszy
- Gabriele Bocchi
- glozow
- Greg Sanders
- Gutflo
- Haoran Peng
- Haowen Liu
- Hennadii Stepanov
- Hodlinator
- i-am-yuvi
- ion-
- ismaelsadeeq
- Jadi
- James O’Beirne
- jb55
- Jeremy Rand
- jlopp
- Jon Atack
- josibake
- jurraca
- Kay
- kevkevinpal
- Kurtis Stirling
- l0rinc
- laanwj
- Larry Ruane
- Léo Haf
- Lőrinc
- luisschwab
- Maciej S. Szmigiero
- Mackain
- MarcoFalke
- marcofleon
- Marnix
- Martin Leitner-Ankerl
- Martin Saposnic
- Martin Zumsande
- Matt Whitlock
- Matthew Zipkin
- Max Edwards
- Michael Dietz
- monlovesmango
- naiyoma
- nervana21
- Nicola Leonardo Susca
- Novo
- omahs
- omg21btc
- pablomartin4btc
- Pieter Wuille
- Pithosian
- R E Broadley
- Randall Naar
- RiceChuan
- rkrux
- romanz
- Roman Zeyde
- Ryan Ofsky
- Sebastian Falbesoner
- secp512k2
- Sergi Delgado Segura
- shiny
- Shunsuke Shimizu
- Simon
- Sjors Provoost
- Skyler
- stickies-v
- Suhas Daftuar
- tdb3
- TheCharlatan
- theStack
- tianzedavid
- Tomás Andróil
- Torkel Rogstad
- Vasil Dimov
- w0xlt
- wgyt
- willcl-ark
- yancy
- zaidmstrr